Schedule Your Consultation with Dr. Prasad Here
- Home
- About Dr. Prasad
- Face & Eyes
Eyelifts
- Eyelid Surgery
- Eye lift Before and After Photos
- Asian Eyelid Surgery
- Upper Eyelid Surgery
- Upper Eyelid Hollow / Lower Brow Hollowing
- Under Eye Bag Surgery
- Eyelid Ptosis Surgery
- Transconjunctival Blepharoplasty
- Under Eye Fillers
- Eyelid Surgery Revision Specialist
- Thyroid Eye Disease
- Tear Trough Implants
- Eye Lift Questions and Answers
- Body
- Injectables
- Laser
- Hair Restoration
- Photos
- Hair Restoration Before and After Photos
- Eye lift Before and After Photos
- Upper Blepharoplasty Before and After
- Ptosis Surgery Before And After
- Facelift Before and After Photos
- Lip Enhancement Before and After Photos
- Under Eye Filler Before and After
- Blepharoplasty Before and After
- Lower Blepharoplasty Before and After Photos
- Eyelid Surgery Before and After
- Double Eyelid Surgery Before and After
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Dr. Prasad
- Face & Eyes
Eyelifts
- Eyelid Surgery
- Eye lift Before and After Photos
- Asian Eyelid Surgery
- Upper Eyelid Surgery
- Upper Eyelid Hollow / Lower Brow Hollowing
- Under Eye Bag Surgery
- Eyelid Ptosis Surgery
- Transconjunctival Blepharoplasty
- Under Eye Fillers
- Eyelid Surgery Revision Specialist
- Thyroid Eye Disease
- Tear Trough Implants
- Eye Lift Questions and Answers
- Body
- Injectables
- Laser
- Hair Restoration
- Photos
- Hair Restoration Before and After Photos
- Eye lift Before and After Photos
- Upper Blepharoplasty Before and After
- Ptosis Surgery Before And After
- Facelift Before and After Photos
- Lip Enhancement Before and After Photos
- Under Eye Filler Before and After
- Blepharoplasty Before and After
- Lower Blepharoplasty Before and After Photos
- Eyelid Surgery Before and After
- Double Eyelid Surgery Before and After
- Contact Us
Hair Transplant
Hair Loss Specialist in New York
Hair Loss specialist Dr Amiya prasad performs hair transplant surgery on patients seeking to treat Androgenetic Alopecia (genetic male pattern hair loss). As a Board Certified Cosmetic and Oculofacial Plastic Surgeon, Dr. Prasad helps patients who’ve lost their hair with hair transplants using methods including FUT or FUE.
In addition, Dr Prasad uses his unique TrichoStem® Hair Regeneration system in combination with hair transplantation to improve the healing time, reduce the loss of hair grafts, and thicken existing thinning hair. This method is not used in traditional hair transplantation. If you’re interested in restoring your hair, learn more here and contact us to see if you’re the right candidate.
What is hair transplant?
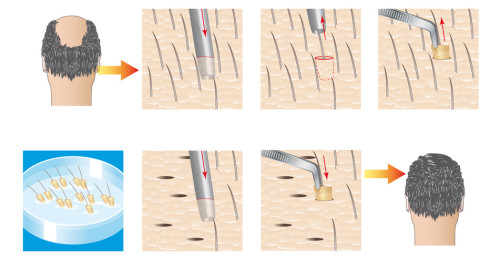
Hair transplant is a cosmetic procedure performed on men and women who have significant hair loss, thinning hair, or bald spots where hair no longer grows. Generally, the procedure consists of moving hair that is genetically resistant to thinning from a small area at the back of the head (donor area) to the recipient area at the front of the scalp. It’s generally recommended to concentrate the transplanted hair to the front of the scalp to help frame your face.
There are two main types of hair transplant processes used today which differ in how donor hair is extracted from a back of the scalp. The method of placement of the hair grafts is essentially the same depending on the preference of the surgeon. The method of harvesting does have an effect on hair graft survival. Either transplant method can be used to harvest the same number of hair grafts, but the procedures differ in the quality of hair grafts harvested and the longevity of graft survival.
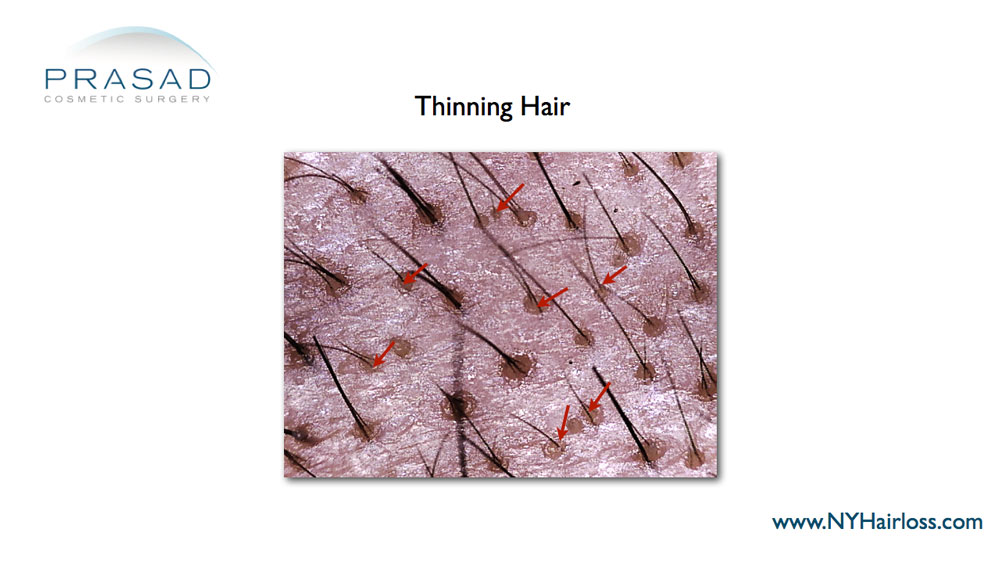
Hair Loss Causes
In men, hair loss and baldness are most commonly due to genetic factors (a tendency passed on in families) and tend to increase with age. Male pattern baldness, in which the hairline gradually recedes to expose more and more of the forehead, is the most common form of hair loss in men.
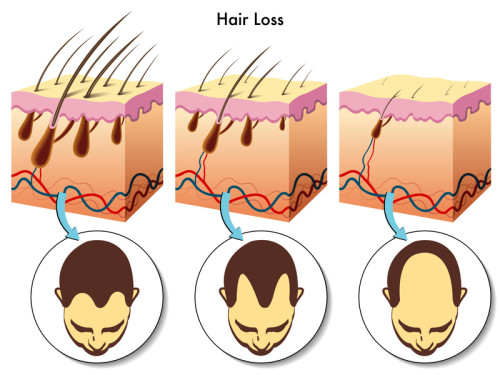
Men may also experience a gradual hair thinning at the crown or very top of the head. For women, the causes of hair loss is more commonly associated with hormonal changes after menopause and usually manifests as thinning of hair throughout the entire head.
According to the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery , 35 million men and 21 million women are experiencing hair loss in the United States. An estimated 80,000 men get a hair transplant each year. Hair transplantation surgery can also be done to replace hair loss due to burns, injury, or diseases of the scalp.
Hair Transplant by Numbers
Hair grows naturally in the scalp in small groups of hair called follicular units. Each follicular unit can have 1-4 hairs averaging about 2.2 hairs. A single transplant session can range from 2000-4000 hairs, depending on an individual’s donor hair density.
In comparison, at the peak of hair health in the early teens, a person has about 100,000 hairs. Hair loss is typically first noticed when 50% of hair has already been lost. A hair transplant operation moves a small percentage of total hair which is a limitation of any hair transplant surgery.
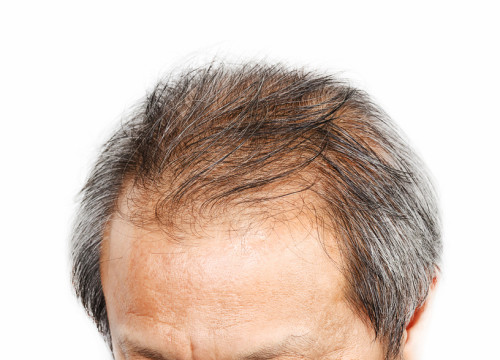
Who is a Good Candidate for Hair Transplant?
Depending on your current level of hair loss, various hair restoration techniques can be used to treat your condition.
It is important to understand that a hair transplant, regardless of the technique or technology used, is a procedure that is strictly limited by the rate of your hair loss progression and the amount of hair you have in your donor area.
It’s important when considering a hair transplant that you should also consider stabilizing the progression of your hair loss. If your hair is thinning significantly, a hair transplant is not advised since your hair will continue to thin, and the multiple transplants needed to keep up with your loss will deplete your donor area. TrichoStem® Hair Regeneration is the preferred option for men and women with thinning hair. The best candidate for a hair transplant is someone who desires hair in an area that has had long standing hair loss, and whose hair loss has been stabilized.
The right candidates for hair transplantation have the following characteristics:
- Good health
- Enough hair in the donor area
- Male. Females can have transplants, but typically females are not good candidates because female pattern hair loss is more diffuse. When hair is diffuse, placing hair grafts close to native hair puts the native hair at risk of loss.
- 30-years-old or older. People who experience hair loss in their late teens and 20s usually have rapid hair loss, so hair grafts can’t match the amount of hair continually being lost.
Stages of Hair Loss
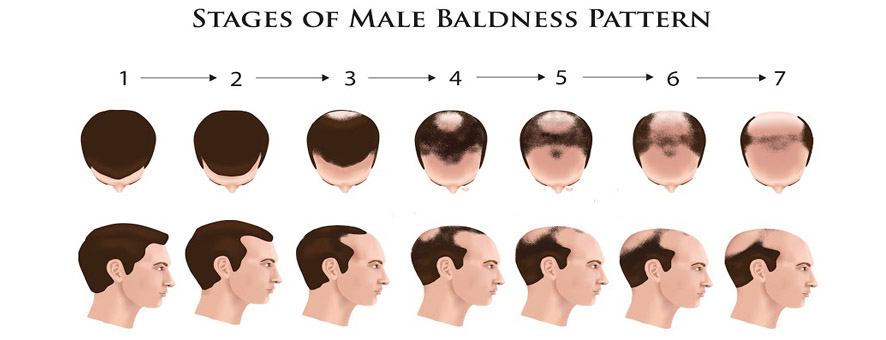
How to prepare for hair transplant surgery?
Although hair transplantation is a safe procedure, some risks do exist which need to be understood. It is important to inform your physician about any medications currently being taken and about previous allergic reactions to drugs or anesthetic agents. Patients with blood clotting disorders also need to inform their physician about their condition before the procedure is performed.
Typically, a narrow strip of skin from the back of the scalp is removed containing genetically resistant to thinning hair follicles. Within the strip are naturally-occurring groups of hair follicles called Follicular Units, which are meticulously dissected under microscopes into 1-4 hair follicular units.
The follicular units are then precisely implanted into the bald areas in the front and top of the head. In some cases, Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE Hair Transplantation) may be used but it requires that the patient have the sides and back of the scalp shaved in order to harvest the grafts before hair transplantation.
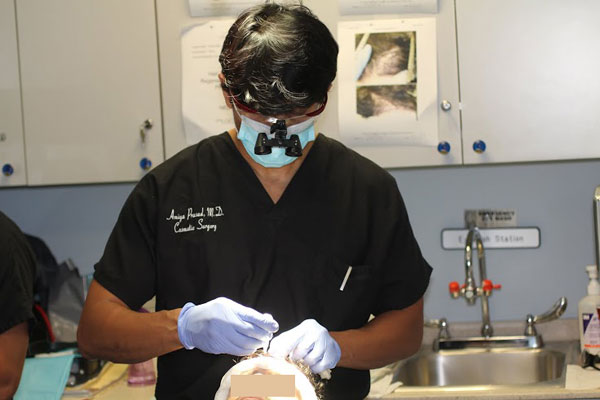
At specific times during the procedure, Dr. Prasad uses his Hair Regeneration method to the donor area, and to areas of the scalp where hair has been transplanted.
The combination of wound healing technology using platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and ACell’s extracellular matrix (ECM) help heal the donor area where the strip of skin was removed, and improve the healing and survival of transplanted hairs on the scalp.
Hair transplantation methods : FUE vs FUT
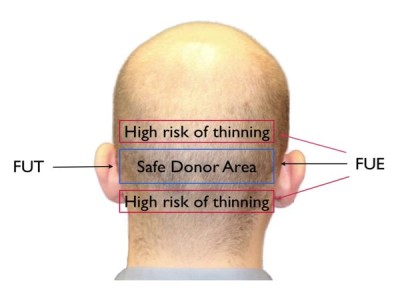
Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT):
Commonly referred to as the “strip method”, follicular unit transplant (FUT) is the more traditional hair transplant method. All hair restoration surgeons will agree that even if it is an older method, it yields more viable hair grafts than the newer and more technologically “advanced” follicular unit extraction (FUE) method.
The FUT procedure involves surgical removal of the strip of skin that holds hairs that are genetically resistant to thinning (the donor area). The strip is then placed under a microscope so follicular units can be harvested.
Since the FUT only takes hairs from the safe donor area, the FUT does have a higher survival rate of grafts when compared to the follicular unit extraction (FUE) method, which takes some hairs from outside the safe donor area which are prone to hair thinning.
In addition, it’s well known that 30% or more of FUE grafts are transected (even with advanced “technology”). “Transected” means that the dermal papilla (or root) is cut away from the graft. This is comparable to planting a tree without the root.
Survival of each follicular unit is dependent on preserving the soft, fatty tissue at the base of the hair that contains the root called the dermal papilla. After graft harvesting, the follicular units are placed on desired areas of the scalp using an implanting tool such as the Choi Implanter.
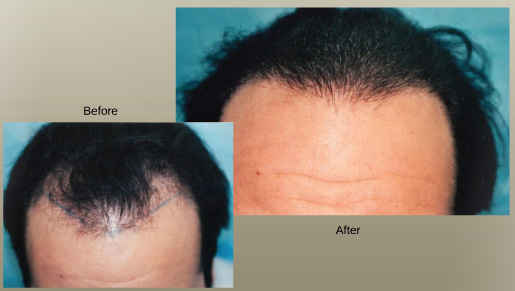
FUT is the Preferred Hair Transplant Procedure at Prasad Hair Restoration
The FUT is the preferred transplant procedure of Prasad Hair Restoration because it yields better quality grafts, has less incidence of graft damage (known as transection), and because the strip scar at the back of the head can potentially heal with minimal scarring using Dr. Prasad’s advanced wound healing techniques and cosmetic surgery closure.
FUE ( Follicular Unit Extraction) – Avoiding the Strip Incision
Follicular unit extraction (FUE) transplantation is considered a more “modern” hair transplant procedure assisted with technologies promoted as superior to “old” FUT methods. The FUE was conceived as a way to avoid the strip scar of FUT procedures.
The FUE extracts follicular units individually from the back of the scalp to avoid the larger FUT donor area scar. However, the FUE method trades off smaller scars in place of the one long extraction scar (which can now have enhanced healing with regenerative medicine technology).
The FUE is a procedure that can be done manually with a hair graft punch, and also robotically with the ARTAS FUE robot. The robot selects the best hairs for extraction faster than a human identifying the best hairs to extract.
Once grafts are harvested, hairs are implanted in the same or similar manner as done with the FUT procedure. FUE technology may imply that it is a superior hair transplant method, but technology does not change the size of the donor area, or the amount of available and viable hair grafts.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) Disadvantages:
- With FUEs, follicular units are extracted using tools and punches that can retrieve the hair shaft, but may cut the root beneath the skin (since you can’t see through the skin). The loss or damage of the root (dermal papilla) known as transection. As much as 30% of hair grafts in an FUE can be damaged at the root, resulting in grafts that don’t take, die, or just don’t grow.
- Less quality grafts – since the FUE doesn’t yield as many grafts in the true genetically resistant donor area as the FUT. A significant number of FUE grafts have to be harvested from outside the narrow genetically resistant zone of hair. Harvesting grafts from outside the donor area means that these hairs are not genetically resistant and more prone to hair thinning and loss.
- Higher incidence of broken grafts – Extracting hair grafts in an FUE procedure is riskier to the graft than during an FUT procedure. Follicular units can be carefully extracted in the strip method since the skin is no longer attached to the body, preserving the all important root, or dermal papilla.
- Longer procedure – the FUE is a longer hair surgery procedure than the FUT. FUT extractions are faster since the strip of hair is removed and hair grafts are prepared by technicians. In the FUE, the patient experiences each individual extraction which is a long and uncomfortable process compared to FUT. In fact, FUE surgery can take twice as long as an FUT.

Hair Transplant Recovery Time, Aftercare, and Healing
Prior to your hair transplant surgery, you’ll be provided instructions about your aftercare and recovery. It’s important you provide your doctor and medical team all information about your health, current medications, smoking and alcohol history, allergies and previous surgeries and dental procedures. Medications may be prescribed for you as part of your aftercare.
If you’re undergoing FUT surgery, allow your hair length in the back to grow at least to 1 inch so the hair can cover your hair transplant scar. Hair transplant recovery in the first few days is managed by limiting strenuous activity and resting with your head elevated when you sleep or relaxing.
You’ll be instructed on how to minimize the hair transplant scar in the donor area and how to manage the hair transplant scabs where the hair grafts were placed. You will be seen in about 1 to 2 weeks for examination, suture removal and examination of your hair transplant scar in the back of the scalp and the appearance of the hair grafts.
Most people are able to return to work after 1 to 2 weeks depending on the type of surgery you undergo and the type of work you do.
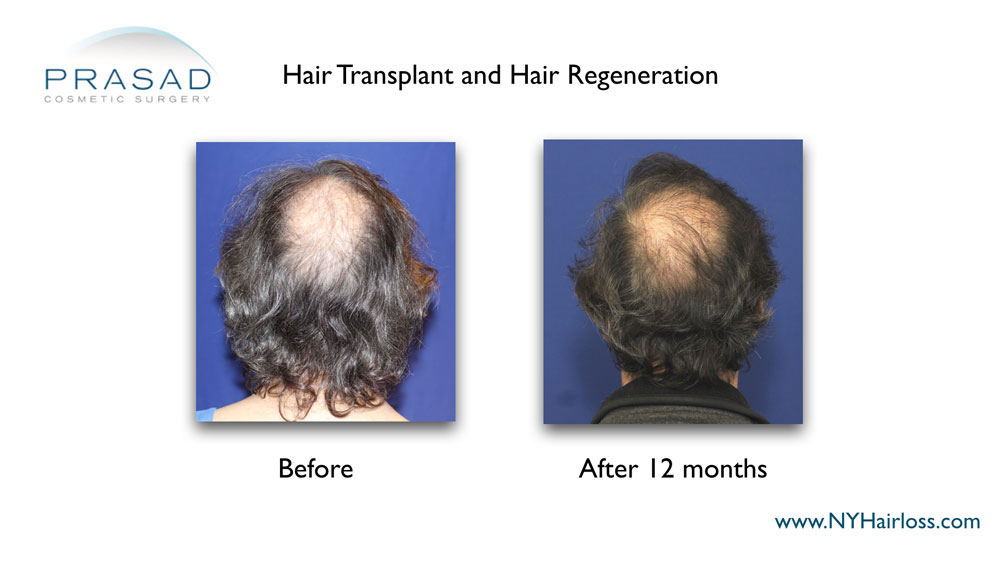
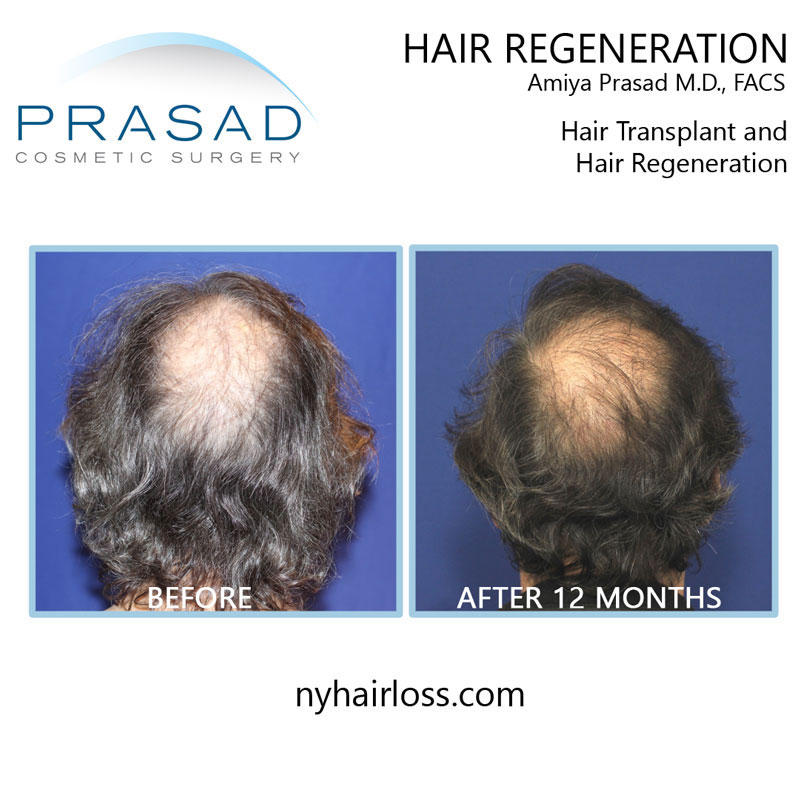
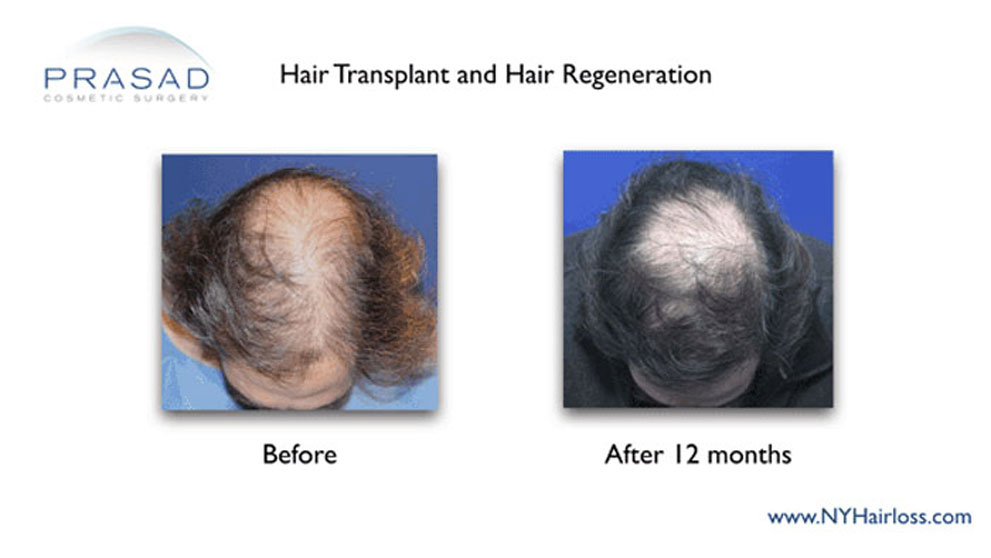
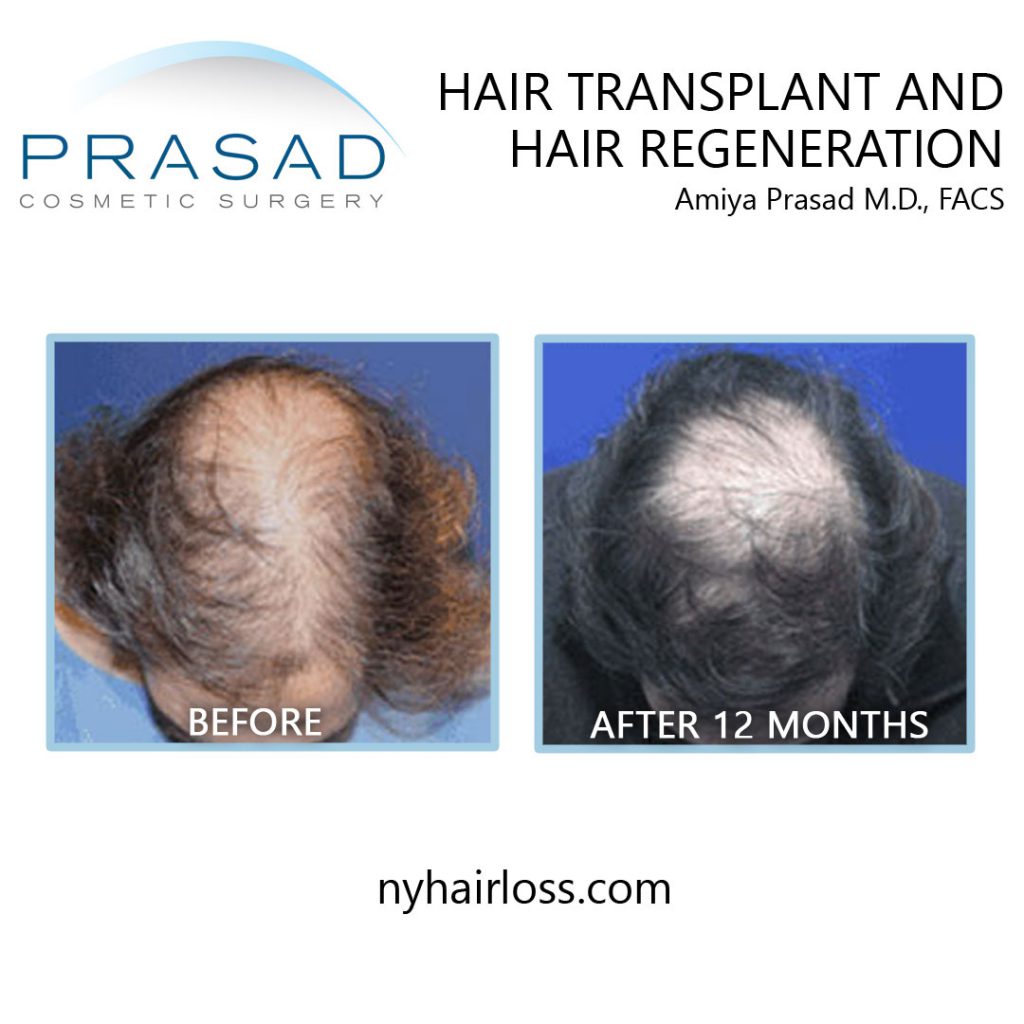
Hair Transplant Alternative: Trichostem for Hair Regeneration
The Hair Regeneration treatment was developed by Dr. Amiya Prasad to thicken existing hair and prevent progressive hair loss. This treatment involves injections which clinically appear to apply the wound-healing properties of an extracellular matrix by ACell, platelet-rich plasma and vitamin D which result in thickening of thinning hair.
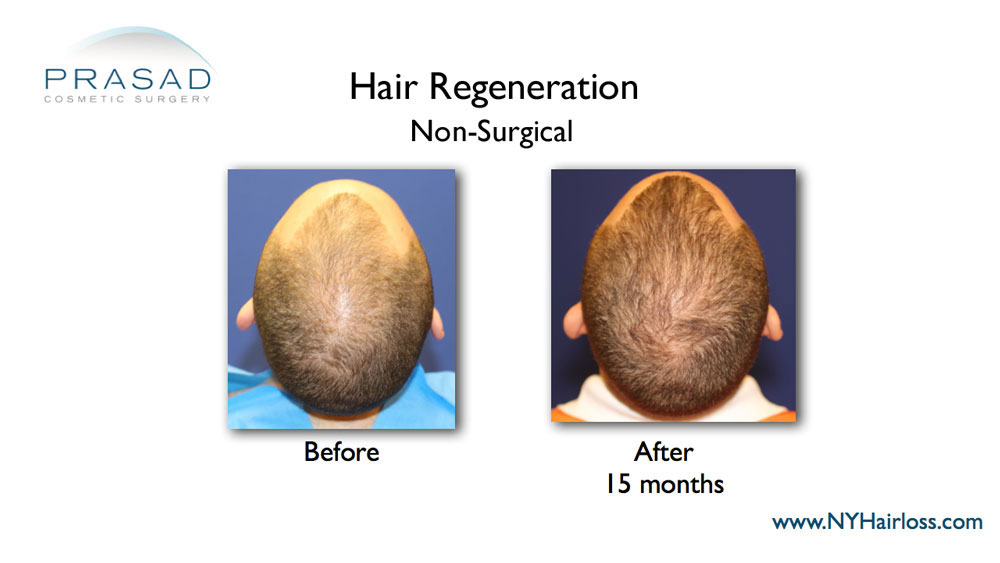
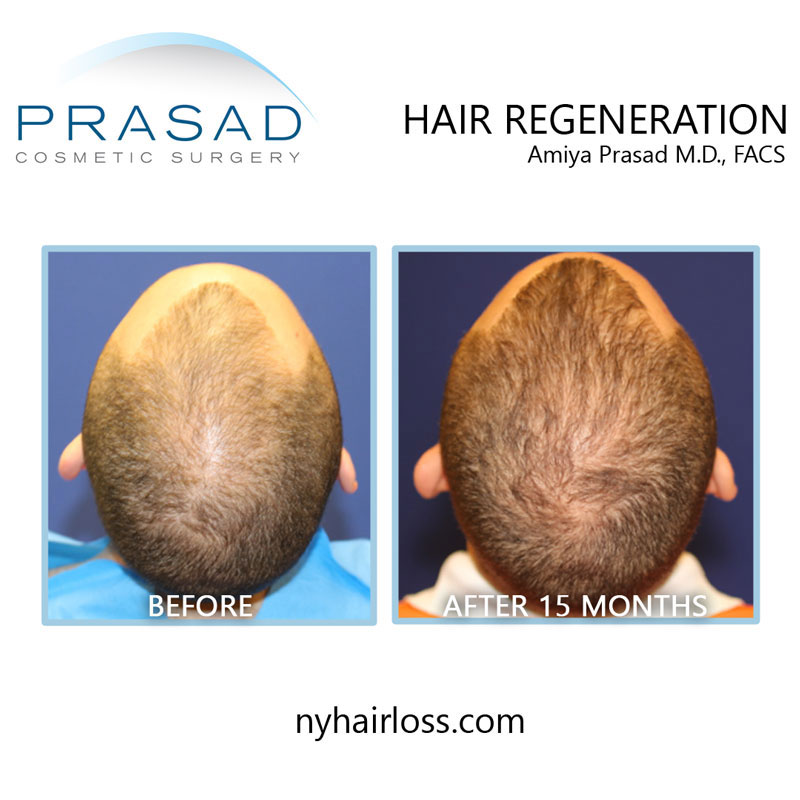
The Hair Regeneration treatment can be used as a replacement for hair transplantation in younger patients by stopping hair loss progression early on and thickening already thinning hair.
This hair loss treatment can also be used to improve graft survival in hair transplants and stop further hair loss (based on approximately 5 years of data – additional injection may be necessary to optimize and maintain results).
The Hair Regeneration treatment has seen success in over 99% of men and women treated for pattern hair loss over the last 7 years, and results have been shown to last 2-5 years, and beyond.
Hair Transplant Limitations
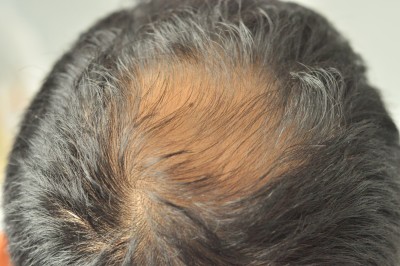
- Limited amount of genetically resistant hair in the donor area
Hair that is genetically resilient to hair loss only grows in a limited area at the back of the head. Any hair taken above or below this area is vulnerable to hair loss after a transplant or as part of progressive hair loss. Given this scenario, it is easy to see the limitations of having to harvest hair from a small area in order to cover a much larger area of baldness at the front of the scalp and the crown.
- Hair transplants do not stop hair thinning
The main problem of hair transplantation is that they do not actually treat the progression of hair loss, since they do not directly address the hormones or other cellular signals that affect hair growth. It is important to understand that hair loss does not occur suddenly.
Rather, hair progressively grows thinner each time hair sheds and enters the growing phase. Hair grows in cycles and with every cycle, hair continues to miniaturize, until it eventually disappears.
- Inadequate density of transplanted hair
Most hair loss sufferers ideally want to achieve natural-looking hair density and coverage in a single session when undergoing a hair transplant. This is an unrealistic expectation, since only a limited amount of hair can be safely and effectively transplanted per square centimeter of the scalp.
Keep in mind that each transplanted hair comes with the entire follicular unit, including the dermal papilla and other soft tissue. These need enough space and blood and nutrient supply in order to grow, therefore, crowding grafts together is not a wise option. Native hairs may also be subjected to trauma during a hair transplant, which can also affect hair density.
Treatments to Maximize Hair Transplant Results
There are known ways in order to maximize the result of an hair transplant surgery, which consist of medical therapy and regenerative medicine or adult stem cell based treatment.
Finasteride Oral Medication
Finasteride (or Propecia) prevents the enzyme 5-alpha reductase from converting testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which affects DHT sensitive hairs in some men. Consistent use of finasteride can help in slowing down hair loss; however, finasteride has been known not to work on all men. There is also an increasing concern of its long-term sexual side effects, which is one reason that many men are refusing to take finasteride. Finasteride must be taken daily for efficacy.
Minoxidil Topical Application
Minoxidil (or Rogaine/Regaine) is a liquid or foam treatment that can be used by both men and women. Minoxidil works by prolonging the anagen (growing) phase of hair and suspending the telogen (shedding and resting) phase. Minoxidil does not thicken hair, nor does it actually stop hair thinning, rather, more hair is retained on the scalp, giving greater density and hair coverage. Minoxidil must be used regularly to sustain effectiveness, although not everyone responds to it as a treatment.
Patient Review on Hair Regeneration








Hair transplant Q&A
The term “hair plugs” refers to a perception many people have of individuals they see and identify as having had a hair transplant. In the past, this perception was related to the large size of hair grafts in otherwise bald scalp.
This perception with modern hair transplant is typically due to existing hair thinning and disappearing, leaving behind the hair grafts. This loss of density causes the grafts to look more obvious. Therefore, it is important to stabilize hair loss so native hair doesn’t thin and disappear, leaving behind isolated hair grafts.
Hairs transplanted from the true donor zone, once healed and growing should continue to grow for the rest of your life. Unfortunately, without additional treatment, existing hair (native hair) will continue to thin and eventually disappear.
Most of the time, when people seek out a hair transplant, they are not informed that there is a high likelihood that they will need more sessions in order to achieve satisfactory results. The most common reasons for multiple hair transplant procedures are due to the following:
A patient’s existing natural hair will continue to thin out until they are lost, leaving behind only the transplanted hairs. If a patient does not have another hair transplant to address the added hair loss, they will be at risk for the “pluggy look”.
Transplanted hair that remains are genetically resistant to the effects of DHT that cause hair thinning and loss. However, native hair is still prone to hair thinning and can be lost years after the transplant was performed.
The donor area itself is limited because only 1500-4000 grafts can be harvested safely in one transplant session. To ensure that the hair grafts survive and grow, only a limited number of hairs can be transplanted so the donor area can heal before having another procedure.
The safe donor area of hair genetically resistant to hair thinning is very limited.
In our experience, the cost of hair transplant has become commoditized in a cost per graft model. This makes people believe that all hair transplants are the same. This is not true. We believe that the best approach is to place the maximal number of hairs from a donor area while at the same time create a minimal scar in the donor area.
Every patient has different variables which affect the number of hairs available for transplantation. A proper examination by the operating surgeon (not a “consultant”) is critical for you to understand what your results will most likely be. Making the right choice is critical. Your donor area is limited. You need to maximize your odds for the best result for you.
